
With bone window we avaluate petrous bone status, Radiologists should examine the external mastoid cortex for osteolysis and subperiosteal abscess evidences and CT with contrast should be used to discard it. If acute coalescent mastoiditis is suspected, Treatment of coalescent mastoiditis requieres intravenous antibiotics and drainage of the subperiosteal abscess. It is usually solved by using antibiotic treatment.Ĭoalescent mastoiditis is diagnosed when temporal bone CT demonstrates erosion of the mastoid septa or mastoid walls.

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may help due to its high sensitivity for detecting extraaxial fluid collections and associated vascular problems.ĬT demonstrates middle ear fluid and opacification of the mastoid air cells,
#HALO THERAPY AND CELLULITIS PLUS#
On the basis of the clinical features and imaging findings,ĭisease will be managed administrating antibiotics intravenously or by using drainage plus antibiotic therapy. Patients affected have prolonged symptoms of media otitis with retroauricular pain,ĬT should be performed early in the course of the disease to classify the mastoiditis as incipient or coalescent and to further detect intracranial complications. Urgent CT is required in severe otalgia caused by acute otomastoiditis with suspected clinical complications and malignant external otitis.Īcute mastoiditis appears as a result of mastoid antrum obstruction.
Surgical drainage may be necessary in impaired area. Orbital cellulitis is treated with intravenous antibiotic therapy however, Meningitis and intracranial abscess formation. When cellulitis is caused by ethmoid sinusitis we must assess by using bone window,ĭehiscence of the lamina papyracea and administer intravenous contrast to discard subperiosteal abscess.Ĭlassical complications of orbital cellulitis may include superior ophthalmic vein and cavernous sinus thrombosis, Retrobulbar stranding and extraconal lentiform fluid collection adjacent to the orbital wall with mass effect upon medial rectus muscle and stranding and streaking intraconal fat. Related symptoms are similar to those observed with periorbital cellulitis, Orbital cellulitis and subperiosteal abcesses frequently occurs as consequence of paranasal sinusitis (ethmoidal). Orbital cellulitis involves the postseptal soft tissues, Periorbital cellulitis is normally treated with oral antibiotics.
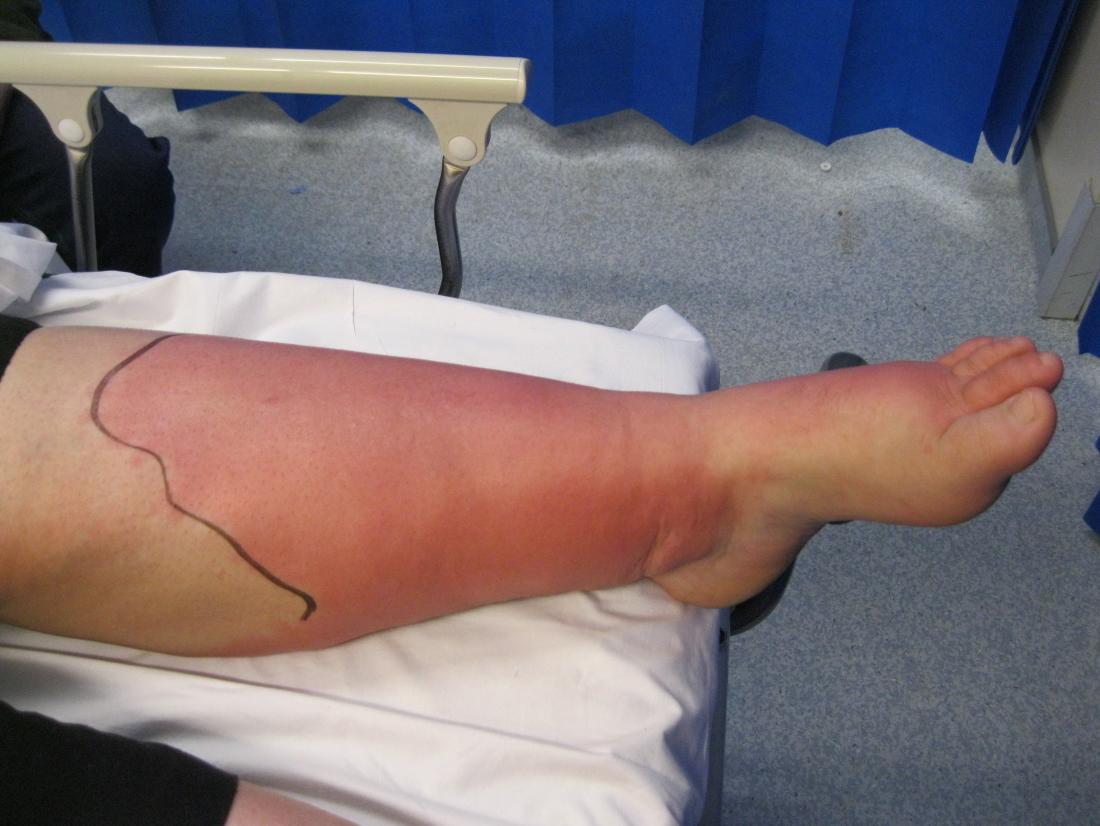
Is limited to the soft tissues anterior to the orbital septum and often results from contiguous spread of an infection of the face,Ĭhemosis and possible limitation of eye movement in the absence of proptosis.ĬT demonstrates diffuse soft-tissue thickening and enhancement areas anterior to the orbital septum. In these conditions CT is important to differentiate preseptal from postseptal cellulitis because they will require different treatment. Periorbital (preseptal) and orbital (postseptal) cellulitis are differentiated by their location in relation to the orbital septum.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
